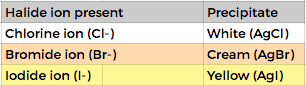
i Cl-, Br- and I- using dilute nitric and silver nitrate solution
Testing for Halide ions by precipitation. Method:
- Add dilute nitric acid
- Add dilute silver nitric acid
- Check the precipitate colour
ii SO4 2- (sulphate ions) using dilute hydrochloric acid and dilute barium chloride solution
Method:
- Add dilute hydrochloric acid
- Add dilute barium chloride
- Ba 2+ (aq) + SO4 2 (l)- –> BaSO4 2- (s)
- Barium sulfate precipitate is white – hence the solid symbol at the end
iii CO3 2- , using dilute hydrochloric acid and identifying the carbon dioxide evolved
Method:
- Add and acid to react with the solution under test
- Collect the gas given off by collecting in a test tube
- Test with lime water – if it goes milky, then there is presence of carbonate ions
- Carbonate + acid –> salt + water + carbon dioxide
- CO3 2- (aq) + 2H+ + (aq) –> CO2 (g) + H2O (l)
- It’s the hydrogen ions (H+) which make the solution acidic- therefore causing the solution to bubble and produce carbonate bubbles
